Knowledge base
February 25, 2023
WSUS versus Intune – What’s the difference? (Pros and cons
WSUS versus Intune – What’s the difference? (Pros and Cons). In this article, we introduce WSUS and Intune – utilities to manage patch deployment and planning. Starting with WSUS, it is a software familiar to every user of computers, laptops, etc. Well, the main and most important task is the ability to deploy updates and various patches for Microsoft products. The second product in this article is Intune. All in all, a cloud-based enterprise mobility management (EMM) solution that helps organizations manage and secure mobile devices, computers and applications.
There is an introduction of benefits along with advantages and disadvantages. Next are the main differences between the two software’s. Shall we begin?
Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) is an update service offered by Microsoft for the Windows operating system. Well, it allows administrators to manage and deploy updates to the Windows operating system and other Microsoft products in a controlled and efficient manner.
Second, WSUS helps organizations keep the Windows operating system and other Microsoft products on their network up to date, reducing the risk of security vulnerabilities and improving overall system performance and reliability.
It is also important to note that WSUS is not a replacement for antivirus or endpoint security software, it is just a way to distribute and manage updates across your network.
How to use WSUS.
Using WSUS involves several steps:
1. Install WSUS – WSUS is installed on a Windows Server computer and requires a SQL Server instance to store metadata and settings for updates.
2. Configure WSUS – After you install WSUS, you need to configure it to download updates from Microsoft update servers. This includes specifying which products and languages updates to download and scheduling updates to be downloaded.
3. Approve updates – Even after downloading updates, administrators must review and approve or reject them before deploying them on clients.
4. Group and target updates – Administrators create computer groups called “target groups” and assign updates to specific computer groups.
5. Implement updates : after the update is approved, it is generally implemented in target computer groups.
6. Check update status: Wsus also checks the status of computer updates in a target group, including installed updates, pending updates and updates that are not installed.
7. Maintenance – it needs some maintenance to work properly. This includes cleaning up old updates and rejecting replaced updates, checking the status of WSUS server and client components, and configuring appropriate settings.
All in all, it is also important to plan the infrastructure and resources needed for your implementation before using WSUS. This includes determining where to install the WSUS server, how many clients connect to the server and the network infrastructure needed to support the deployment.
Pros and cons of WSUS
WSUS benefits
- Specifies whether clients can access updated files from the intranet or from the public Microsoft Windows Update site used to support remote clients.
- Updates are distributed to clients in multiple languages.
- An internal server on a private intranet acts as a virtual Windows Update server.
- Implements security updates and patches to keep your system secure and up-to-date by reducing the risk of security problems.
- Saves your organization time and money by reducing the need for manual updates, automating the update process and reducing the need for additional IT resources.
- Administrators manage the bandwidth used to download updates so that updates do not consume too much bandwidth or slow down other network operations.
- Additional reporting and monitoring functions.
- Manages tens/hundreds of computers simultaneously.
WSUS disadvantages
- WSUS has a few reports, but they are limited in scope. Collecting all the reports needed for vulnerability accounting requires employees to spend time compiling reports from multiple sources.
- If WSUS is misconfigured, it also poses security risks, such as malware or other malicious software infiltrating your network.
- The management database sometimes gets corrupted during normal operation, causing the server to crash and need to be cleaned up and restored to fix it.
- WSUS is built primarily for the Windows operating system and other Microsoft products and does not provide support for non-Windows products.
- Third-party software such as Java, Chrome and Adobe are popular targets for hackers because they often contain unpatched vulnerabilities. However, Wsus only allows patches with complex temporary fixes and the catalog of updates is not intuitive.
Next up in this article blog WSUS vs Intune – What’s the difference? we are introducing Intune.
What is Intune?
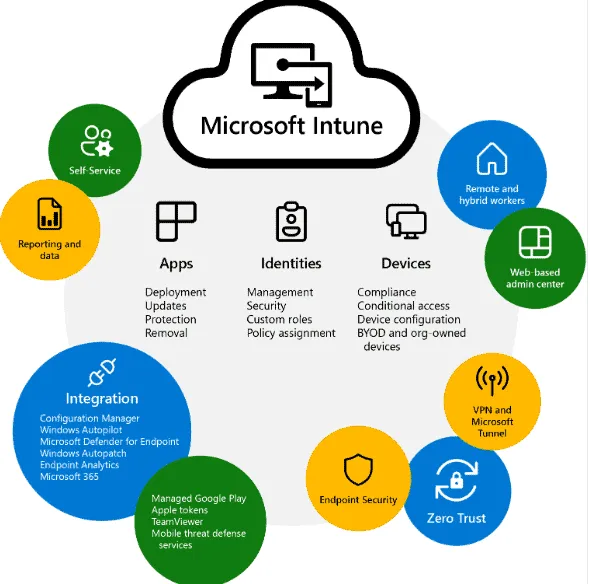
Another software choice is Microsoft Intune. In short, it is Microsoft’s cloud-based service for managing mobile devices (MDM) and mobile applications (MAM).
In addition, it is a great solution for IT administrators to manage and protect corporate data and manage access to corporate applications on personal and business devices. Sure, you use Intune to manage iOS, iPadOS, Android, Windows 10 and macOS devices. It is also used to manage access to Microsoft 365 apps and services.
Intune is also part of the Microsoft 365 platform and can be integrated with other services such as Azure Active Directory and Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager.
How to use Intune.
There are several ways to manage and secure your devices and apps with Microsoft Intune:
Enroll devices: start managing your device with Intune, you need to enroll your device. This is done by using the company portal app on the device on which users register their device. Notably, IT administrators also enroll devices in bulk using the Microsoft Endpoint Manager management center.
Create policies: allows IT administrators to create policies that are applied to specific groups of devices. These policies include security, access and compliance settings.
Distribute applications: this implements apps on devices. IT administrators, in turn, upload apps to the Intune console and then assign them to specific device groups.
Monitoring and troubleshooting: provides various tools for monitoring and troubleshooting devices and applications. For example, IT administrators view device and user information, compliance status and receive alerts about potential problems.
Integrate with other services: integrates with Azure Active Directory, Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager and Microsoft Endpoint Protection to provide a complete solution for device management and access to corporate resources.
Mobile application management: controls access to company apps, sets app security policies and monitors app usage.
Conditional access: sets conditional access policies that allow or block access to corporate resources based on specific conditions, such as device compatibility, location or network.
Identity protection: protects your identity by implementing multiple authentication and configuring Azure AD conditional access policies.
Advantages and disadvantages of Intune
Intune benefits
- Because Intune is a subscription-based service, it can be more cost-effective than buying and maintaining an on-premises solution.
- Multiple security features including device encryption, conditional access and mobile app management to protect corporate data and resources.
- A user-friendly interface for end users through the enterprise portal app to enroll devices, install apps and track compliance status.
- Clearly, it gives IT administrators the flexibility to manage devices and applications, whether the devices are for business or personal use and whether users are in the office or working remotely.
- Helps IT administrators ensure that devices and applications comply with corporate policies and industry regulations.
- Easy to set up and use, has a user-friendly interface and the ability to create policies using templates.
- Intune users have full access to technical support 24/7.
Intune disadvantages
- Too little focus on mobile devices, so no full system management platform.
- A feature set to handle complex package implementations is missing.
- Has many features and settings, and it can take IT administrators time to learn how to use them effectively.
- Offers a variety of options for device and app management, but customization options have some limitations, especially compared to on-premises solutions.
- Difficult to implement and configure, especially for large organizations with many devices and users.
- No support for the Linux operating system.
We have arrived at the comparison section of WSUS versus Intune – What is the difference?
WSUS versus Intune
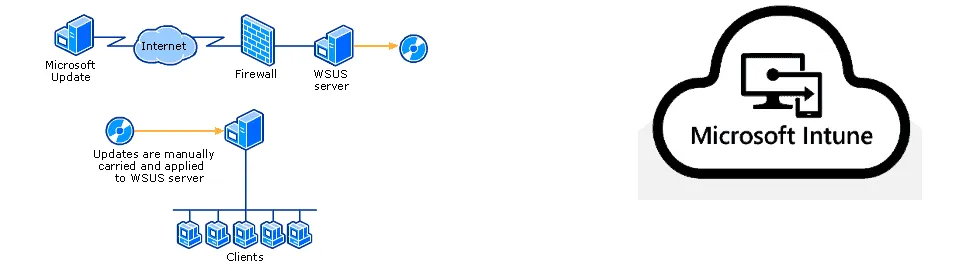
Importantly, WSUS is a Windows-only solution that manages updates for Windows systems and requires an on-premises infrastructure. Intune is a cloud service that manages updates and devices across multiple platforms and requires no on-premises infrastructure.
WSUS (Windows Server Update Services) and Intune are both used explicitly to manage and deploy software updates, but they have some important differences:
Device Manager
On the one hand, WSUS is primarily used to manage updates for Windows devices on an enterprise network, while Intune is used to manage updates for various devices, including Windows, iOS and Android.
Scalability
Here, WSUS is a server-based product installed on a Windows Server. Furthermore, it handles a large number of clients within the organization’s network, but its scalability is limited by the hardware resources of the server on which it is installed. As the number of clients increases, so does the amount of disk space needed to store update files.
Intune, on the other hand, is a cloud service built on Azure and designed to work on many devices. It automatically scales based on the number of devices it manages and does not have the same disk space limitations as WSUS. In addition, Intune also allows you to manage devices remotely, eliminating the need to maintain on-premises infrastructure as your organization grows.
Implementation
Moreover, WSUS requires dedicated servers and infrastructure to be set up and maintained, while Intune is a cloud service that can be easily configured and managed via the cloud.
Supports
For this, WSUS is primarily used to manage updates for Windows devices on corporate networks. So it only supports Windows operating systems, including Windows 10, 8.1, 8, 7, Vista, Server 2012 and Server 2008.
Otherwise, Intune is a cloud service you use to manage updates across multiple devices, including Windows, iOS and Android. It supports Windows 10, 8.1 and 7 and supports all current versions of iOS and Android.
Cost
Of particular note, WSUS is a free server product from Microsoft that allows administrators to manage and distribute updates for Windows systems.
But Microsoft Intune is a cloud-based service and not free. A paid service that charges based on the number of devices being managed. It also includes additional features such as mobile device management and application management.
Safety
Wsus and Intune are used to improve security by keeping systems and devices up-to-date with the latest security patches, but they have several strengths. Importantly, WSUS focuses primarily on patch management, while Intune focuses on mobile device management and security.
Thanks for reading WSUS versus Intune – What’s the difference? (Pros and Cons). We will now conclude the article.
WSUS versus Intune – What’s the difference? Conclusion
In short, WSUS is a good solution for managing Windows updates within a Windows-only environment, while Intune is a better solution for managing updates and devices across multiple platforms and for organizations that do not want to maintain an on-premises infrastructure. Finally, it is important to assess your organization’s specific needs and requirements before making a decision.
Source: cloud infrastructure services
Want to know more?
Related
blogs
Tech Updates: Microsoft 365, Azure, Cybersecurity & AI – Weekly in Your Mailbox.